Sarcee Family Dental is dedicated to helping you achieve the smile you have always wanted! If you have any questions about bone grafts or sinus lifts, or the bone grafting or sinus lift procedure, or you would like to schedule a consultation appointment to discuss whether you might need a bone graft or sinus lift, please contact the dedicated Sarcee Family Dental team at (403) 233-7369 and we will be happy to help.
Choose Sarcee Family Dental
Your SW Calgary Choice for Quality Bone Grafting
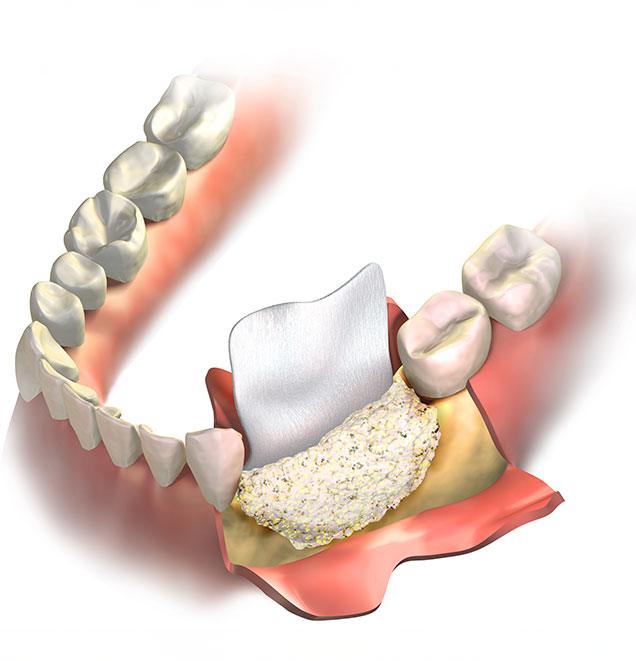
If you have tooth decay, disease, injury or facial damage that has affected your jaw, bone grafting may be necessary to add volume and density to your jaw bone, while also improving stability. Sarcee Family Dental is pleased to offer bone grafting to help you achieve the dental health and wellness you deserve.

Sarcee Family Dental
What is Bone Grafting?
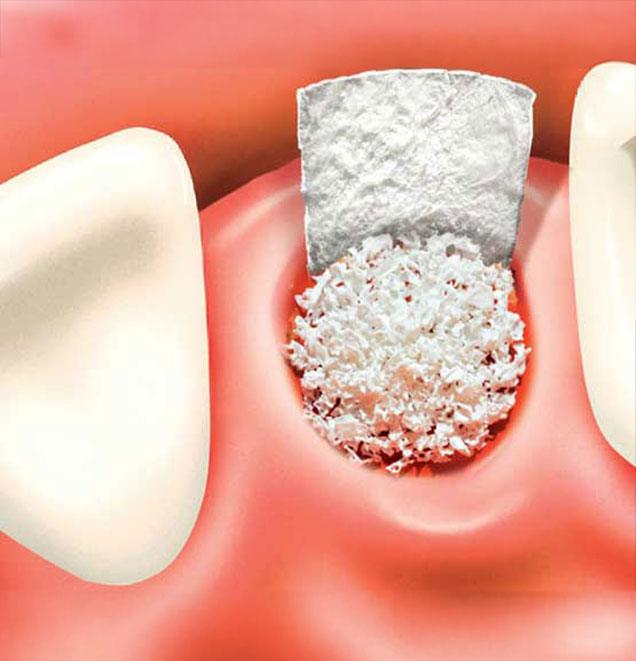
If you have insufficient bone tissue to support your teeth or dental implants, a dental bone graft may be required. Bone grafts help to reinforce the dental bone that is responsible for stabilizing your teeth. By stabilizing the bone structure, the facial profile and overall oral function can be preserved. In a majority of cases, bone grafting is used to enhance the jawbone in preparation for accommodating a dental implant, or for preserving natural teeth in that area where the bone loss is negatively affecting neighboring teeth.
At Sarcee Family Dental, the bone grafting procedure begins with comprehensive X-rays to assess the extent of bone loss and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. To ensure optimal comfort, a local anesthetic is administered at the start of the procedure. A small incision is then made in the gum tissue, allowing access to the jawbone. The jawbone is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected. Depending on your case, various materials may be used for grafting, such as tissue sourced from your own body, a tissue bank or synthetic substitutes. Your dentist will determine the most suitable option to facilitate bone tissue regeneration effectively.
Once the graft material is placed, the gum tissue is carefully repositioned and sutures are used to close the incision site. The grafting material serves to support and encourage your body’s natural bone regeneration process. During the healing period, which may involve minor discomfort, swelling and bruising for a few days, pain relievers can help manage any symptoms. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to prevent infection, which should be taken as directed. Most patients experience minimal discomfort during recovery, provided post-operative instructions are followed diligently to ensure optimal healing and successful outcomes.

Sarcee Family Dental
Sinus Lift
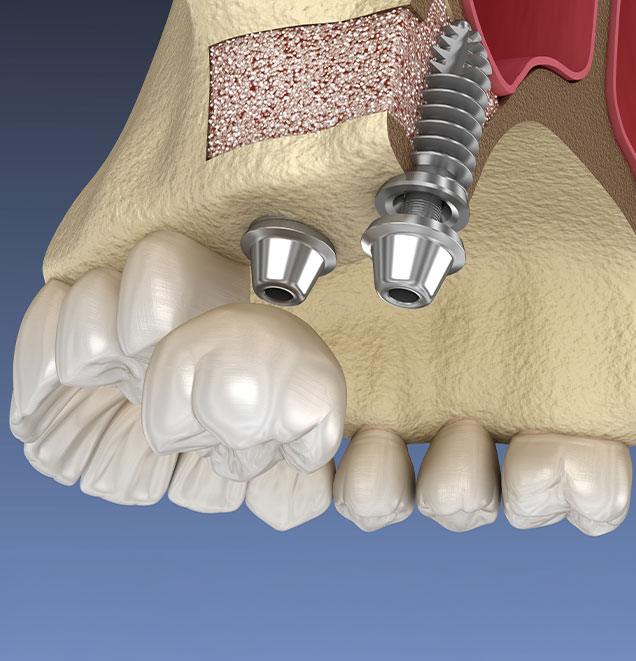
A sinus lift, also known as sinus augmentation, is a surgical procedure used in implant dentistry to increase bone volume in the upper jaw. It involves lifting the sinus membrane and placing bone graft material in the space between the jaw and the sinus cavity. This procedure is typically recommended for patients with periodontal disease, natural bone loss or insufficient bone height due to tooth loss. By augmenting bone in the posterior maxilla, sinus lifts create a stable foundation for dental implants, ensuring successful placement and integration. The procedure begins with a thorough evaluation, including imaging studies like X-rays or CT scans, to assess sinus and jawbone anatomy. During the procedure, the Sarcee Family Dental team carefully lifts the sinus membrane and inserts the bone graft material. Depending on your needs, the graft may come from your own body, donor tissue or synthetic materials. After the procedure, you will receive post-operative care instructions and medications to manage discomfort and promote healing. Sarcee Family Dental is pleased to offer sinus lifts, which provide a reliable and effective solution for restoring bone volume in the upper jaw.

SARCEE FAMILY DENTAL
We look forward to hearing from you soon
Call the dedicated Sarcee Family Dental team at (403) 233-7369 to schedule your Bone Grafting appointment today.